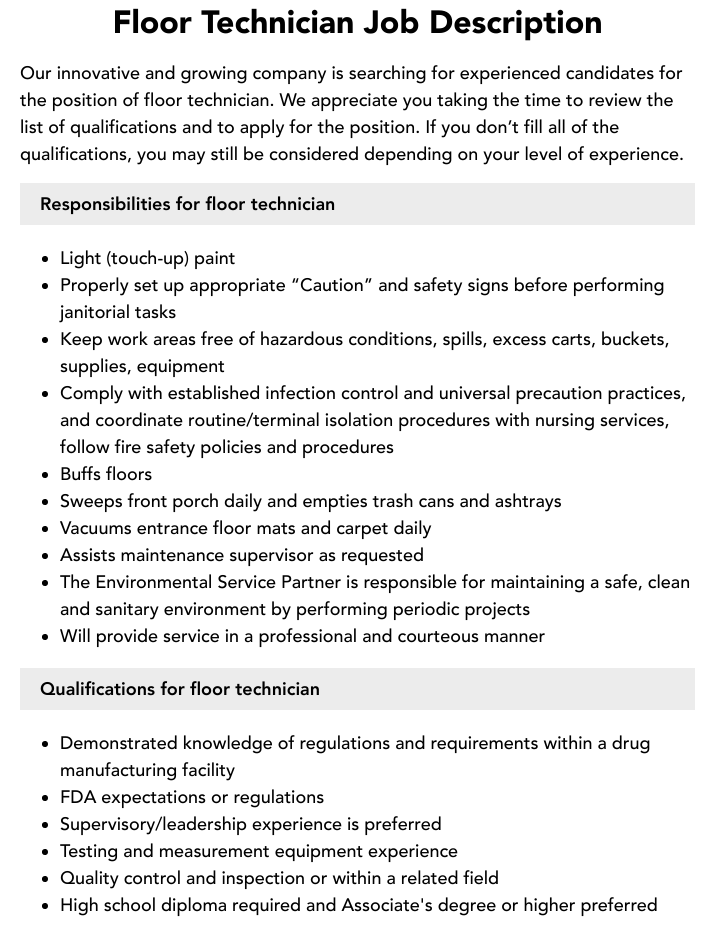
An instructional designer job description outlines the roles and responsibilities of a professional responsible for designing, developing, and evaluating instructional materials and learning experiences. It serves as a guide for potential candidates and hiring managers to understand the requirements and expectations of the position.
Instructional designers play a crucial role in creating effective and engaging educational content. They work closely with subject matter experts, educators, and other stakeholders to analyze learning needs, develop instructional strategies, and design learning materials that align with specific learning objectives. Their work contributes to improved learning outcomes, increased learner satisfaction, and efficient knowledge transfer.
The field of instructional design has evolved significantly over the years, driven by advancements in technology and changing pedagogical approaches. Instructional designers now utilize a range of tools and methodologies to create interactive and personalized learning experiences that cater to diverse learner needs and preferences.
To perform their duties effectively, instructional designers typically possess a combination of technical skills, such as proficiency in instructional design software and learning management systems, and soft skills, such as strong communication, collaboration, and problem-solving abilities.
Overall, an instructional designer job description provides a detailed overview of the responsibilities, qualifications, and impact of the instructional design profession, guiding individuals and organizations in the recruitment and management of these professionals.
1. Analysis
In the context of instructional design, analysis plays a pivotal role in ensuring that learning experiences align with the specific needs and characteristics of learners. This facet of an instructional designer job description encompasses various responsibilities and implications.
-
Identifying Learning Needs:
Instructional designers conduct thorough needs assessments to pinpoint the knowledge, skills, and attitudes that learners require to achieve desired learning outcomes. This involves gathering data from multiple sources, such as surveys, interviews, and observations, to gain a deep understanding of the learners’ current knowledge levels, learning preferences, and motivations. -
Understanding Learner Characteristics:
Instructional designers analyze learner characteristics, including their cognitive abilities, learning styles, cultural backgrounds, and prior experiences, to tailor learning experiences accordingly. This understanding helps them create content that is accessible, engaging, and relevant to the diverse needs of learners. -
Developing Learner Profiles:
Based on the analysis of learning needs and learner characteristics, instructional designers develop learner profiles that provide a comprehensive picture of the target audience. These profiles guide the design and development of learning materials and activities that are customized to the specific learning requirements and preferences of the learners. -
Evaluating Learning Effectiveness:
Instructional designers evaluate the effectiveness of learning experiences by collecting and analyzing data on learner performance, satisfaction, and knowledge retention. This ongoing evaluation process helps them identify areas for improvement and make data-driven decisions to enhance the quality of learning materials and experiences.
In summary, the analysis facet of an instructional designer job description highlights the importance of understanding learning needs and learner characteristics to create effective and targeted learning experiences. By conducting thorough needs assessments, analyzing learner profiles, and evaluating learning effectiveness, instructional designers ensure that learning materials and activities align with the specific requirements and preferences of learners, ultimately leading to improved learning outcomes.
2. Design
The design aspect of an instructional designer job description encompasses the development of instructional strategies and learning materials that align with specific learning objectives and learner needs. It involves a systematic process of creating engaging and effective learning experiences that cater to the diverse learning preferences and styles of learners.
Instructional designers begin by identifying the most appropriate instructional strategies for the subject matter and learning context. This may involve selecting from a range of approaches, such as collaborative learning, problem-based learning, or blended learning, to ensure that the learning experience is both effective and engaging. They then design learning materials that support the chosen strategies, such as interactive simulations, online discussions, or hands-on activities.
The development of learning materials involves careful consideration of factors such as visual design, accessibility, and cultural sensitivity. Instructional designers use a variety of tools and technologies to create visually appealing and accessible materials that cater to diverse learners, including those with disabilities or language barriers. They also ensure that the materials are culturally appropriate and respectful of different backgrounds and perspectives.
By effectively designing instructional strategies and learning materials, instructional designers play a crucial role in facilitating meaningful learning experiences. They create learning environments that are conducive to knowledge acquisition, skill development, and positive attitudes towards learning.
In summary, the design aspect of an instructional designer job description highlights the importance of developing effective instructional strategies and learning materials that align with learning objectives and learner needs. Instructional designers use a systematic and creative approach to design engaging and accessible learning experiences that promote successful learning outcomes.
3. Development
In the context of instructional design, development refers to the process of creating and producing learning content that aligns with specific learning objectives and learner needs. Instructional designers engage in various activities to develop high-quality learning materials that facilitate effective learning experiences.
-
Content Creation:
Instructional designers create a wide range of learning content, including online courses, interactive simulations, videos, and printed materials. They use their expertise in instructional design principles and learner psychology to ensure that the content is engaging, accessible, and effective. -
Media Selection:
Instructional designers select appropriate media and technologies to deliver learning content effectively. They consider factors such as learner preferences, the nature of the content, and the learning context when choosing media, such as videos, animations, or interactive simulations. -
Prototyping and Piloting:
Instructional designers often create prototypes and pilot versions of learning materials to test their effectiveness and gather feedback from learners. This iterative approach allows them to refine and improve the content before its final release. -
Collaboration:
Instructional designers frequently collaborate with subject matter experts, graphic designers, and other professionals to develop learning content. They work closely with these stakeholders to ensure that the content is accurate, engaging, and aligned with the desired learning outcomes.
The development facet of an instructional designer job description highlights the crucial role of instructional designers in creating high-quality learning content. By skillfully applying instructional design principles, selecting appropriate media, and engaging in iterative development processes, instructional designers contribute to the creation of effective and engaging learning experiences that promote successful learning outcomes.
4. Evaluation
Evaluation is a crucial aspect of instructional design, ensuring that learning materials and experiences meet their intended objectives and effectively contribute to learner growth. Within the context of an instructional designer job description, evaluation plays a vital role in several key areas:
-
Measuring Learning Outcomes:
Instructional designers evaluate learning materials and experiences to assess whether they are achieving the desired learning outcomes. This involves collecting and analyzing data on learner performance, knowledge retention, and satisfaction to determine the effectiveness of the learning intervention. -
Identifying Areas for Improvement:
Evaluation helps instructional designers identify areas where learning materials and experiences can be improved. By analyzing learner feedback, performance data, and other metrics, instructional designers can pinpoint weaknesses and make data-driven decisions to enhance the quality of the learning experience. -
Iterative Design Process:
Evaluation is an integral part of the iterative design process in instructional design. Instructional designers use evaluation results to refine and improve learning materials and experiences over time. This ongoing process ensures that the learning intervention remains effective and aligned with evolving learner needs and advancements in instructional strategies. -
Demonstrating the Impact of Learning:
Evaluation provides evidence of the impact of learning materials and experiences, which is essential for stakeholders such as educators, administrators, and funding organizations. Instructional designers use evaluation results to demonstrate the value of their work and justify the investment in learning and development initiatives.
In summary, evaluation is an essential component of an instructional designer job description as it enables instructional designers to assess the effectiveness of their work, identify areas for improvement, engage in iterative design, and demonstrate the impact of learning materials and experiences. By conducting rigorous evaluations, instructional designers ensure that learning interventions are effective, engaging, and aligned with the desired learning outcomes.
5. Collaboration
Collaboration is a cornerstone of instructional design, as it involves working closely with a diverse range of stakeholders to ensure that learning materials and experiences are effective, engaging, and aligned with real-world needs.
-
Subject Matter Experts:
Instructional designers collaborate with subject matter experts (SMEs) to ensure the accuracy and depth of learning content. SMEs provide invaluable insights into the subject matter, helping instructional designers develop materials that are both informative and engaging. -
Educators:
Instructional designers work with educators to understand the specific needs and learning styles of the target audience. Educators provide feedback on learning materials and activities, ensuring that they align with pedagogical best practices and meet the diverse needs of learners. -
Stakeholders:
Instructional designers collaborate with stakeholders, such as administrators, managers, and community members, to gather input and ensure that learning materials and experiences are aligned with organizational goals and community needs.
Effective collaboration enables instructional designers to create learning solutions that are relevant, engaging, and impactful. By working closely with subject matter experts, educators, and stakeholders, instructional designers gain a comprehensive understanding of the learning context, learner needs, and desired outcomes, ultimately leading to the development of high-quality learning experiences.
FAQs on Instructional Designer Job Description
This section addresses frequently asked questions about instructional designer job descriptions, providing clear and concise answers to common concerns and misconceptions.
Question 1: What are the essential responsibilities of an instructional designer?
Instructional designers are responsible for analyzing learning needs, designing and developing learning materials, and evaluating the effectiveness of learning experiences. They collaborate with subject matter experts, educators, and stakeholders to ensure that learning materials are aligned with organizational goals and learner needs.
Question 2: What qualifications are typically required for instructional designer jobs?
Instructional designers typically hold a master’s degree in instructional design, education, or a related field. They also possess strong communication, collaboration, and problem-solving skills, as well as proficiency in instructional design software and learning management systems.
Question 3: What industries hire instructional designers?
Instructional designers are employed in various industries, including education, corporate training and development, healthcare, government, and non-profit organizations. They work in both public and private sector settings.
Question 4: What is the job outlook for instructional designers?
The job outlook for instructional designers is positive, with projected growth in the coming years. This growth is driven by the increasing demand for online learning and the need for organizations to improve employee training and development.
Question 5: What are the career advancement opportunities for instructional designers?
Instructional designers can advance their careers by taking on leadership roles, specializing in a particular area of instructional design, or pursuing further education. They may also transition to related fields such as learning and development management or educational technology.
Question 6: How can I prepare for a career as an instructional designer?
To prepare for a career as an instructional designer, you can earn a degree in instructional design, education, or a related field. You can also gain experience through internships, volunteer work, or by creating your own learning materials. Additionally, staying up-to-date on the latest instructional design trends and technologies is essential.
These FAQs provide a comprehensive overview of instructional designer job descriptions, addressing common questions and providing valuable insights into the profession.
Transition to the next article section: Exploring the Importance of Instructional Design
Tips for Crafting an Effective Instructional Designer Job Description
A well-crafted instructional designer job description is crucial for attracting qualified candidates and ensuring a successful hiring process. Here are some tips to help you create an effective job description:
Tip 1: Clearly Define the Role
Start by clearly outlining the responsibilities and duties of the instructional designer. Include specific tasks such as conducting needs assessments, designing learning materials, developing and delivering training programs, and evaluating learning outcomes.
Tip 2: Specify Required Qualifications
List the minimum qualifications required for the position, including education, experience, and skills. Consider including both hard skills (e.g., proficiency in instructional design software) and soft skills (e.g., communication and collaboration).
Tip 3: Use Clear and Concise Language
Write the job description in a clear and concise manner, using specific and measurable terms. Avoid using jargon or technical language that may be unfamiliar to potential candidates.
Tip 4: Highlight the Impact of the Role
Emphasize the impact of the instructional designer’s work on the organization. Explain how the role contributes to the achievement of learning and training goals.
Tip 5: Include a Call to Action
End the job description with a clear call to action, inviting qualified candidates to apply for the position. Provide contact information and instructions on how to submit applications.
Tip 6: Proofread Carefully
Before posting the job description, proofread it carefully for any errors in grammar, spelling, or formatting. A well-written job description reflects positively on your organization and attracts top talent.
Tip 7: Seek Feedback
Consider seeking feedback from colleagues, HR professionals, or potential candidates to ensure that the job description is clear, accurate, and effective.
Tip 8: Update Regularly
As the organization’s needs and the instructional design field evolve, update the job description accordingly to ensure that it remains relevant and attractive to qualified candidates.
By following these tips, you can create an effective instructional designer job description that attracts qualified candidates and helps you build a strong team of instructional design professionals.
Transition to the article’s conclusion: The Importance of a Well-Crafted Instructional Designer Job Description